Design description:
The target of this project was the design of a small portable mixer supplied by a 9V PP3 battery, keeping high quality performance.
The mixer is formed assembling three main modules that can be varied in number and/or disposition to suit everyone needs.
The three main modules are:
Input Amplifier Module: a low noise circuit equipped with a variable voltage-gain (10 - 100) pre-set, primarily intended as high quality microphone input, also suitable for low-level line input.
An optional, Balanced Input Amplifier Module with similar features was added on request.
Tone Control Module: a three-band (Bass, Middle, Treble) tone control circuit providing unity-gain when its controls are set to flat frequency response. It can be inserted after one or more Input Amplifier Modules and/or after the Main Mixer Amplifiers.
Main Mixer Amplifier Module: a stereo circuit incorporating two virtual-earth mixers and showing the connection of one Main Fader and one Pan-Pot.
The image below shows a Block diagram of the entire mixer featuring four Input Amplifier Modules followed by four in-out switchable Tone Control Modules, one stereo Line input, four mono Main Faders, one stereo dual-ganged Main Fader, four Pan-Pots, a stereo Main Mixer Amplifier Module and two further Tone Control Modules switchable in and out for each channel, inserted before the main Left and Right outputs.
Obviously this layout can be rearranged at everyone wish.
An astonishing feature of this design lies in the fact that a complete stereo mixer as shown below in the Block diagram draws less than 6mA current!
Block diagram:
Input Amplifier Module
Circuit diagram:
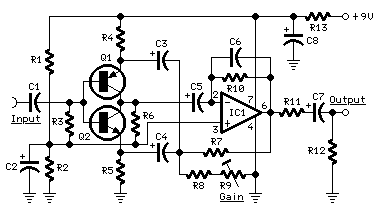
Parts:
R1,R2,R7_______22K 1/4W Resistors R3,R4,R5_______47K 1/4W Resistors R6______________4K7 1/4W Resistor R8,R13________220R 1/4W Resistors R9______________2K 1/2W Trimmer Cermet (See Notes) R10___________470K 1/4W Resistor R11___________560R 1/4W Resistor R12___________100K 1/4W Resistor C1____________470nF 63V Polyester Capacitor C2,C8_________100µF 25V Electrolytic Capacitors C3,C4,C5________2µ2 63V Electrolytic Capacitors C6_____________47pF 63V Ceramic Capacitor C7______________4µ7 63V Electrolytic Capacitor Q1____________BC560C 45V 100mA Low noise High gain PNP Transistor Q2____________BC550C 45V 100mA Low noise High gain NPN Transistor IC1___________TL061 Low current BIFET Op-Amp
Circuit description:
The basic arrangement of this circuit is derived from the old Quad magnetic pick-up cartridge module. The circuit was rearranged to cope with microphone input and a single-rail low voltage supply.
This low-noise, fully symmetrical, two-transistor head amplifier layout, allows the use of a normal FET input Op-Amp as the second gain stage, even for very sensitive microphone inputs.
The voltage-gain of this amplifier can be varied by means of R9 from 10 to 100, i.e. 20 to 40dB.
Notes:
- R9 can be a trimmer, a linear potentiometer or a fixed-value resistor at will.
- When voltage-gain is set to 10, the amplifier can cope with 800mV peak-to-peak maximum Line levels.
- Current drawing for one Input Amplifier Module is 600µA.
- Frequency response is 20Hz to 20KHz - 0.5dB.
- Total Harmonic Distortion measured with voltage-gain set to 100: 2V RMS output = <0.02% @ 1KHz; <0.04% @ 10KHz.
- Total Harmonic Distortion measured with voltage-gain set to 10 & 33: 2V RMS output = <0.02% @ 1KHz & 10KHz.
- THD is much lower @ 1V RMS output.
- Maximum undistorted output voltage: 2.8V RMS.
Balanced Input Amplifier Module
Circuit diagram:
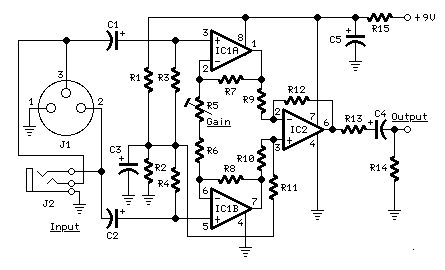
Parts:
R1,R2__________22K 1/4W Resistors R3,R4___________2K2 1/4W Resistors R5______________2K 1/2W Trimmer Cermet (See Notes) R6____________180R 1/4W Resistor R7,R8,R9,R10___10K 1/4W Resistors R11,R12________10K 1/4W Resistors R13___________560R 1/4W Resistor R14___________100K 1/4W Resistor R15___________100R 1/4W Resistor C1,C2,C4_______10µF 25V Electrolytic Capacitors C3,C5_________100µF 25V Electrolytic Capacitors IC1___________LM833 Low noise Dual Op-Amp IC2___________TL061 Low current BIFET Op-Amp J1_____________XLR3 Socket J2____________6.3mm Stereo Jack Socket
Circuit description:
This optional circuit is a transformerless differential input microphone preamplifier, operating at single-rail low voltage supply. Avoiding transformers has several advantages, including lower cost, smaller physical size, and reduced distortion. The circuit is formed by the two op-amps contained in the LM833 High-Performance chip (IC1), amplifying the input signal before the common-mode noise is cancelled in the differential amplifier (IC2). The equivalent input noise is about 760 nV over a 20 Hz to 20 kHz frequency band (-122 dB referred to 1V), which is over 26 dB lower than a typical microphone's output from the 30dB SPL ambient noise level in a quiet room. THD is under 0.02% at maximum gain, and less than 0.01% at minimum gain.
The voltage-gain of this amplifier can be varied by means of R5 from 8 to 100, i.e. 18 to 40dB.
Notes:
- R5 can be a trimmer, a linear potentiometer or a fixed-value resistor at will.
- When voltage-gain is set to 8, the amplifier can cope with 920mV peak-to-peak maximum Line levels.
- Current drawing for one Input Amplifier Module is 4mA.
- Frequency response is flat from 15Hz to 20KHz.
- Total Harmonic Distortion measured with voltage-gain set to 100: 2V RMS output = <0.02% @ 1KHz; & 10KHz.
- Total Harmonic Distortion measured with voltage-gain set to 20: 2V RMS output = <0.01% @ 1KHz & 10KHz.
- Maximum undistorted output voltage: 2.6V RMS.
Tone Control Module
Circuit diagram:
Parts:
P1,P2_________100K Linear Potentiometers P3____________470K Linear Potentiometer R1,R2,R3_______12K 1/4W Resistors R4,R5___________3K9 1/4W Resistors R6,R7___________1K8 1/4W Resistors R8,R9__________22K 1/4W Resistors R10___________560R 1/4W Resistor R11___________100K 1/4W Resistor R12___________220R 1/4W Resistor C1______________1µF 63V Polyester Capacitor C2_____________47nF 63V Polyester Capacitor C3,C5___________4n7 63V Polyester Capacitors C4_____________22nF 63V Polyester Capacitor C6,C8_________100µF 25V Electrolytic Capacitors C7______________4µ7 63V Electrolytic Capacitor IC1___________TL061 Low current BIFET Op-Amp
Circuit description:
This is a straightforward design using the Baxandall-type active circuitry slightly modified to obtain a three-band control. Total voltage gain of this module is 1 when controls are set in their center position.
Notes:
- Current drawing for one Tone Control Module is 400µA.
- Frequency response is 20Hz to 20KHz - 0.5dB, controls flat.
- Tone control frequency range: ±15dB @ 30Hz; ±19dB @ 1KHz; ±16dB @ 10KHz.
- Total Harmonic Distortion measured @ 2V RMS output = <0.012% @ 1KHz; <0.03% @ 10KHz.
- THD is below 0.01% @ 1V RMS output.
- Maximum undistorted output voltage: 2.5V RMS.
Main Mixer Amplifier Module
Circuit diagram:
Parts:
P1,___________100K Linear Potentiometer P2_____________10K Linear Potentiometer R1,R2,_________15K 1/4W Resistors R3,R4,R11,R12_100K 1/4W Resistors R5,R6__________22K 1/4W Resistors R7,R8_________390K 1/4W Resistors R9,R10________560R 1/4W Resistors R13___________220R 1/4W Resistor C1,C2_________330nF 63V Polyester Capacitors C3,C8_________100µF 25V Electrolytic Capacitors C4,C5__________10pF 63V Ceramic Capacitors C6,C7___________4µ7 63V Electrolytic Capacitors IC1___________TL062 Low current BIFET Dual Op-Amp
Circuit description:
The schematic of this circuit is drawn as a stereo unit to better show the input Main Fader and Pan-Pot connections. The TL062 chip contains two TL061 op-amps into the same 8 pin case and is wired as two virtual-earth mixer amplifiers having a voltage gain of about 4, to compensate for losses introduced in the passive Pan-Pot circuitry. Therefore, total voltage-gain is 1.
Each channel added to the mixer must include the following additional parts:
P1, P2, R1, R2, R3, R4, C1 and C2.
These parts must be wired as shown in the above circuit diagram, connecting R3 and R4 to pin #2 and pin #6 of IC1 for Right and Left channel respectively. These IC1 pins are the "virtual-earth mixing points" and can sum together a great number of channels.
Notes:
- Current drawing for one stereo Main Mixer Amplifier Module is 800µA.
- Frequency response is 20Hz to 20KHz - 0.5dB.
- Total Harmonic Distortion measured @ 2V RMS output = <0.008% @ 1KHz; <0.017% @ 10KHz.
- THD is 0.005% @ 1V RMS output.
- Maximum undistorted output voltage: 2.8V RMS.
Further Parts:
To parts listed above should be added: one Main on-off SPST switch, a LED used as pilot-light with its dropping 2K2 1/4W series-resistor, DPDT switches to enable or omit Tone Control Modules as shown in the Block diagram, input and output connectors of the type preferred, one stereo dual-gang 100K potentiometer to fade the Stereo Line Input as shown in the Block diagram, battery clip, PP3 9V battery, knobs etc.